Book traversal links for 2 Overview of Hawala activity
2 Overview of Hawala activity
Effective from 15/8/2021The FATF defines hawala providers (and other similar service providers) as money transmitters, particularly with ties to specific geographic regions or ethnic communities, that arrange for transfer and receipt of funds or equivalent value and settle through trade, cash, and net settlement over a long period of time. While hawala providers-also known as hawaladars-often use banking channels to settle between them, what makes them distinct from other money transmitters is their use of other settlement methods, including trade, cash, and long-term net settlement.2 Hawala is an activity based on trust and was established to avoid high charges by people who cannot afford them, the ability to reach beneficiaries in remote places quickly where banks do not operate, and the existence of strict currency controls in some countries. Because communication is often by text message and there is no need for funds to clear, hawala transfers may also be available faster than the ones made using the formal financial system. Although hawala providers generally specialize in transferring money between certain jurisdictions, they are also part of larger networks that can arrange transfers to almost any part of the world. Such transfers are likely to be slower and more expensive than transfers within the corridors in which the provider specializes. Although the hawala system minimizes use of the formal financial system, including use of international wires, it is important to note that almost all hawaladars will ultimately seek to conduct transfers, particularly international transfers through LFIs, and possibly to use other financial services. In doing so, they could expose the LFI with which they do business with to the risks of their own business activities and customers.
Common Attributes of Hawala Providers
| ||||||||||||||||||
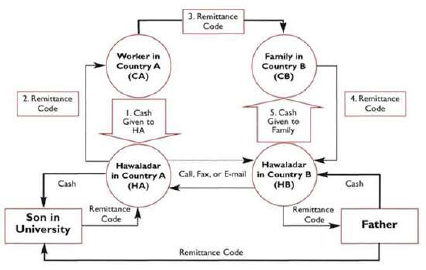
Sample Hawala Transaction:3
2 See also the FATF report The Role of Hawala and Other Similar Service Providers in ML/TF (fatf-gafi.org)
3 Source: IMF III Features of the Informal Hawala System : Informal Funds Transfer Systems : An Analysis of the Informal Hawala System: (imf.org)