Book traversal links for L. Special Cases of Margin Agreements
L. Special Cases of Margin Agreements
C 52/2017 GUI Effective from 1/4/202137. When multiple margin agreements apply to a single netting set, the netting set should be broken down into sub-netting sets that align with the respective margin agreement for calculating both RC and PFE.
38. When a single margin agreement applies to multiple netting sets, RC at any given time is determined by the sum of two terms. The first term is equal to the un-margined current exposure of the bank to the counterparty aggregated across all netting sets within the margin agreement reduced by the positive current net collateral (i.e. collateral is subtracted only when the bank is a net receiver of collateral). The second term is non-zero only when the bank is a net poster of collateral: it is equal to the current net posted collateral (if there is any) reduced by the un-margined current exposure of the counterparty to the bank aggregated across all netting sets within the margin agreement. Net collateral available to the bank should include both VM and NICA. Mathematically, RC for the entire margin agreement is:
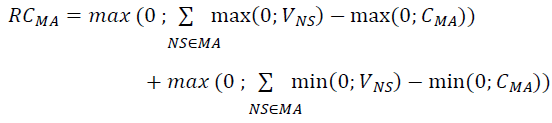
where the summation NS ∈ MA is across the netting sets covered by the margin agreement (hence the notation), VNS is the current mark-to-market value of the netting set NS and CMA is the cash equivalent value of all currently available collateral under the margin agreement.
39. An alternative description of this calculation is as follows:
| Step 1: | Compute the net value, positive or negative, of each netting set. These calculated values correspond to the terms VNS in the expression above. | ||
| Step 2: | Sum the values of all netting sets with positive value, to get Total Positive Value (TPV). This corresponds to the term in the expression above: |
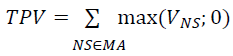
| Step 3: | Sum the values of all of netting sets with negative value, to get Total Negative Value (TNV). This corresponds to the term in the expression above: |
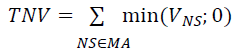
| Step 4: | Calculate the net current cash value of collateral, including NICA and VM. This corresponds to the term CMA in the expression above. If the bank is net holder of collateral, then CMA is positive; it is the net value held (NVH). If the bank is a net provider of collateral, then CMA is negative, and its absolute value is the net value provided (NVP). Note that either NVH>0 and NVP=0, or NVP>0 and NVH=0. | ||
| One of the following cases then applies: | |||
| Step 5a: | If NVH>0 (so NVP=0), then RC = TPV – NVH, but with a minimum of zero – that is, RC cannot be negative. | ||
| or | |||
| Step 5b: | If NVH=0 (so NVP>0), then RC = TPV + NVP – TNV, but with a minimum of TPV – that is, RC cannot be less than TPV. | ||
40. To calculate PFE when a single margin agreement applies to multiple netting sets, netting set level un-margined PFEs should be calculated and aggregated, i.e. PFE should be calculated as the sum of all the individual netting sets considered as if they were not subject to any form of margin agreement.